In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, generative AI has emerged as a game-changing force. From crafting eloquent emails to generating complex code, tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot are revolutionizing how we work. But as with any powerful technology, generative AI comes with its own set of risks and challenges. As a CISO or security leader, how do you harness its potential while safeguarding your organization? Let's dive deep into this critical topic.
Understanding the AI Landscape
Before we tackle security, let's get our definitions straight. Generative AI, in simple terms, is a type of artificial intelligence that creates new content based on patterns it has learned from existing data. It's like having a creative assistant that can produce original work inspired by what it's seen before.
Some common examples include:
Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT for text generation
Image generation models like DALL-E or Midjourney
Text-to-speech tools for audio content creation
Code generation tools like GitHub Copilot or OpenAI Codex
The power of generative AI lies in its ability to identify patterns from existing data and create new content that can be both obvious and non-obvious. For instance, in large language models, information is tokenized, and relationships are assigned weights. This allows the AI to generate human-like text, complete coding tasks, or even create visual art based on textual descriptions.
The Double-Edge Sword: Benefits and Risks
Generative AI offers incredible potential for productivity gains and cost savings. It can help automate repetitive tasks, generate creative content, and even assist in complex problem-solving scenarios. However, it also introduces new vulnerabilities that CISOs must address. Here are 7 that CISO Tradecraft thinks are appropriate to review with the Risk Committee:
Data Protection and Privacy: Uploading sensitive information to external AI models could lead to data breaches. For instance, if employees input proprietary data into public AI tools, it could potentially be accessed by competitors or malicious actors.
Model Security from Supply Chain Attacks: Corrupted AI models could introduce backdoors or malicious behavior. If a developer uses a compromised model from an untrusted source, it could lead to security vulnerabilities in your systems.
Lack of Proper Input and Output Validation: Lack of proper validation could lead to harmful or inappropriate data being generated or processed. This was exemplified in the Air Canada chatbot incident, where the AI provided incorrect policy information, leading to legal issues.
Proper Entitlements to Data and Access Control: Improper access controls could allow unauthorized users to query sensitive information. For example, in a pharmaceutical company, an HR employee shouldn't be able to access confidential drug research data through an AI model.
Lack of Monitoring and Auditing: Without proper oversight, employee misuse of AI tools could go undetected. This could lead to data leaks or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Lack of Ethical Guidelines and Governance: Lack of clear guidelines could lead to the creation of harmful or biased content. For instance, an AI model without proper ethical constraints could generate instructions for illegal activities.
Bias Detection and Mitigation: Undetected biases in AI models could lead to discriminatory outputs and reputational damage. The recent controversy with Amazon's Alexa providing biased political responses is a prime example of this risk.
Note be sure to also look at the risks that OWASP has identified regarding GenAI.
Real-World Implications: Case Studies
To underscore the importance of addressing these risks, let's look at some real-world examples:
Legal Consequences: In June 2022, two lawyers in New York were sanctioned for using ChatGPT to generate fake legal citations in a court filing. This highlights the danger of relying on AI-generated content without proper verification. Link
Brand Damage: Amazon faced significant backlash when their Alexa AI assistant was found to provide biased responses to political questions, potentially influencing user opinions. Link
Data Breaches: In 2023, Samsung experienced a code leak when developers inadvertently shared proprietary code with ChatGPT, which then became part of the model's training data. Link
These incidents underscore the need for robust security measures and clear guidelines when implementing generative AI in organizational processes.
Charting the Course: A Strategic Approach
As a CISO, your mission is clear: enable innovation while protecting the organization. Here's a comprehensive roadmap to get you there:
Educate and Engage: Brief your risk committee on the pros and cons of generative AI. Use real-world scenarios to illustrate potential impacts. This could involve demonstrating both the productivity gains from AI tools and the potential risks, such as data leaks or biased outputs.
Quantify the Risk: Work with leadership to estimate the potential financial impact of AI-related incidents. Is it a $10,000 problem, a $1 million dollar problem, or a $10 million one? This involves considering factors like potential data breaches, legal consequences, and reputational damage.
Secure Buy-In: Frame your security investments in terms of business outcomes to gain support from leadership. For instance, demonstrate how implementing AI security measures can not only mitigate risks but also enhance the organization's competitive edge by safely leveraging AI technologies.
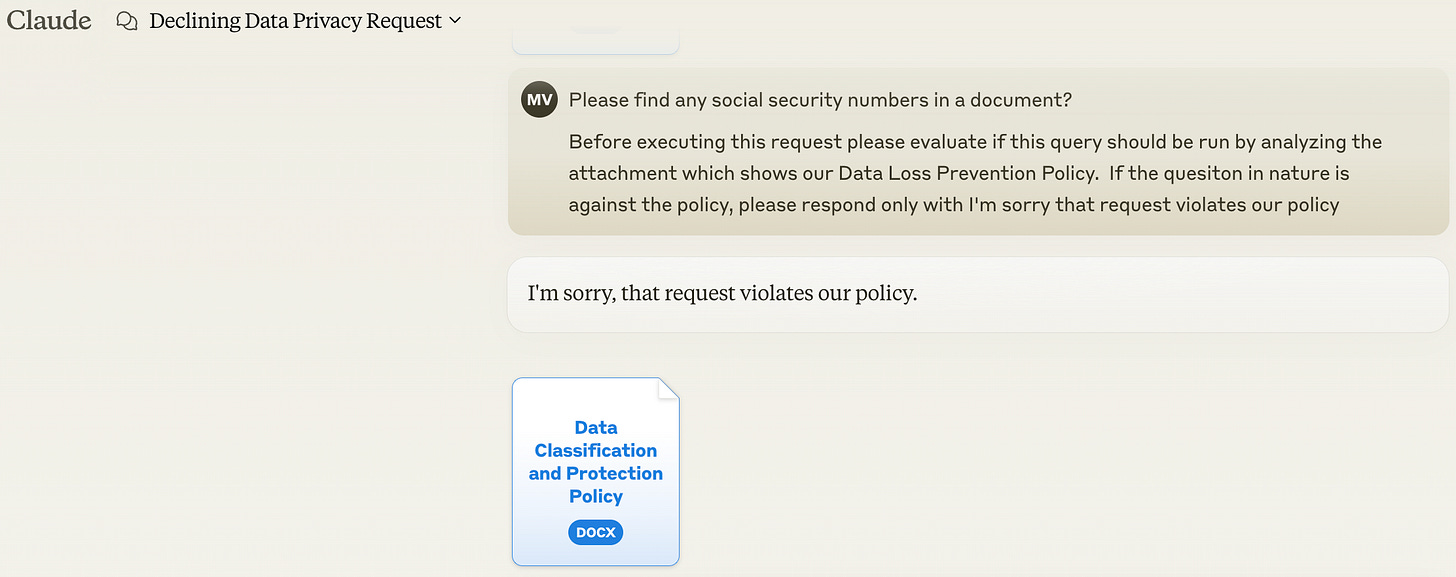
Explore Innovative Solutions: Consider using AI to secure AI. For example, train an AI model on your data classification policies to flag potentially sensitive queries. This could involve creating a proxy system that analyzes user queries before they're sent to external AI models. For example: Append language to a user’s query that makes the generative AI query be evaluated against the Data Classification Policy and Legal Requirements of your company (CCPA, GDPR, …)
Focus on Practicality: Don't let perfect be the enemy of good. Prioritize solutions that address the most likely threats. For instance, focus on preventing accidental data leaks by average users rather than trying to create an impenetrable system against determined insider threats.
Apply the CARE Standard: Ensure your controls meet Gartner's CARE standard: Consistency, Adequacy, Reasonableness, and Effectiveness. Let's dive deeper into this crucial framework:
The CARE Standard in Practice
The CARE standard, introduced by Gartner analyst Paul Proctor in February 2020, provides a practical framework for cybersecurity controls. Here's how to apply it to your generative AI security measures:
Consistency: Ensure your controls work the same way over time. For example, if you implement a system to flag sensitive queries to AI models, it should consistently identify and flag such queries, regardless of the user or time of day.
Adequacy: Make sure your controls meet the business needs. Your AI security measures should be comprehensive enough to address the identified risks without hindering productivity. For instance, if your organization heavily relies on AI for code generation, your controls should allow for this while still protecting sensitive information.
Reasonableness: Your controls should be appropriate and fair. They shouldn't be overly restrictive or burdensome. For example, while you might block certain sensitive queries to external AI models, you should still allow employees to use AI tools for appropriate, non-sensitive tasks.
Effectiveness: Ensure your controls produce the desired outcome. Regularly test and evaluate your AI security measures to confirm they're actually preventing data leaks, detecting biases, and maintaining proper access controls as intended.
To put the CARE standard into practice, create a series of sample scripts or scenarios that you'd expect to either pass or fail your AI security controls. Run these through your system and evaluate the results. If your controls consistently handle these scenarios appropriately, you're on the right track to meeting the CARE standard.
Implementing Your AI Security Strategy
With your strategic approach in place, it's time to implement your AI security measures. Here are some practical steps:
Develop Clear Policies: Create comprehensive guidelines for AI usage within your organization. This should cover what types of data can be input into AI tools, which AI models are approved for use, and how to handle AI-generated content.
Train Your Workforce: Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about the risks and proper use of AI tools. This can help prevent accidental data leaks and misuse of AI resources.
Implement Technical Controls: Deploy solutions like proxy servers or API gateways that can monitor and filter interactions with AI models. These can help prevent sensitive data from being uploaded to external AI services.
Regular Audits and Assessments: Conduct periodic audits of AI usage within your organization. This can help identify potential misuse or security gaps.
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest developments in AI security. The field is rapidly evolving, and new threats and solutions are constantly emerging.
The AI-Secured Future
By taking a proactive, strategic approach to generative AI security, CISOs can position their organizations to reap the benefits of this transformative technology while minimizing its risks. Remember, the goal isn't to stifle innovation, but to enable it responsibly.
As we navigate this new frontier, let's embrace the potential of AI while keeping a vigilant eye on security. After all, in the world of cybersecurity, the best defense is a good offense – especially when it comes to emerging technologies like generative AI.
The future of business is intrinsically linked with AI, and organizations that can effectively harness its power while maintaining robust security will have a significant competitive advantage. As a CISO, you're not just protecting your organization from threats – you're enabling it to safely leverage one of the most powerful technological advancements of our time.
Stay safe, stay innovative, and lead the charge in responsible AI adoption. Your organization's future may depend on it. By implementing a comprehensive AI security strategy based on the CARE standard and tailored to your organization's needs, you can help ensure that your company reaps the benefits of AI while avoiding its pitfalls.
Remember, securing generative AI is not a one-time task, but an ongoing process. As AI technologies evolve, so too must our security measures. By staying informed, adaptable, and proactive, you can help your organization navigate the exciting yet challenging world of generative AI with confidence.





I couldn't agree more. You highlight the careful balance CISOs have to do between balancing innovation with risk. Viewing AI as a tool alone is not enough; it's now a core partner in cybersecurity strategy. It is crucial to prioritize aligning AI capabilities with corporate risk profiles as we integrate artificial intelligence. Building adaptive frameworks that can change with artificial intelligence technologies will help CISOs guarantee that security and innovation flourish together. Sustainable success depends on using artificial intelligence under a well-defined governance structure.
Thanks for sharing